Frequency comb
A frequency comb or spectral comb is a spectrum made of discrete and regularly spaced spectral lines. In optics, a frequency comb can be generated by certain laser sources.
A number of mechanisms exist for obtaining an optical frequency comb, including periodic modulation (in amplitude and/or phase) of a continuous-wave laser, four-wave mixing in nonlinear media, or stabilization of the pulse train generated by a mode-locked laser. Much work has been devoted to this last mechanism, which was developed around the turn of the 21st century and ultimately led to one half of the Nobel Prize in Physics being shared by John L. Hall and Theodor W. Hänsch in 2005.[1][2][3]
The frequency domain representation of a perfect frequency comb is like a Dirac comb, a series of delta functions spaced according to
where is an integer, is the comb tooth spacing (equal to the mode-locked laser's repetition rate or, alternatively, the modulation frequency), and is the carrier offset frequency, which is less than .
Combs spanning an octave in frequency (i.e., a factor of two) can be used to directly measure (and correct for drifts in) . Thus, octave-spanning combs can be used to steer a piezoelectric mirror within a carrier–envelope phase-correcting feedback loop. Any mechanism by which the combs' two degrees of freedom ( and ) are stabilized generates a comb that is useful for mapping optical frequencies into the radio frequency for the direct measurement of optical frequency.
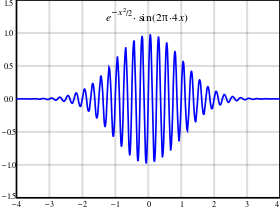
Generation
Using a mode-locked laser
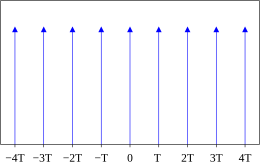
The most popular way of generating a frequency comb is with a mode-locked laser. Such lasers produce a series of optical pulses separated in time by the round-trip time of the laser cavity. The spectrum of such a pulse train approximates a series of Dirac delta functions separated by the repetition rate (the inverse of the round-trip time) of the laser. This series of sharp spectral lines is called a frequency comb or a frequency Dirac comb.
The most common lasers used for frequency-comb generation are Ti:sapphire solid-state lasers or Er:fiber lasers[4] with repetition rates typically between 100 MHz and 1 GHz[5] or even going as high as 10 GHz.[6]
Using four-wave mixing
Four-wave mixing is a process where intense light at three frequencies interact to produce light at a fourth frequency . If the three frequencies are part of a perfectly spaced frequency comb, then the fourth frequency is mathematically required to be part of the same comb as well.
Starting with intense light at two or more equally spaced frequencies, this process can generate light at more and more different equally spaced frequencies. For example, if there are a lot of photons at two frequencies , four-wave mixing could generate light at the new frequency . This new frequency would get gradually more intense, and light can subsequently cascade to more and more new frequencies on the same comb.
Therefore, a conceptually simple way to make an optical frequency comb is to take two high-power lasers of slightly different frequency and shine them simultaneously through a photonic-crystal fiber. This creates a frequency comb by four-wave mixing as described above.[7][8]
In microresonators
An alternative variation of four-wave-mixing-based frequency combs is known as Kerr frequency comb. Here, a single laser is coupled into a microresonator (such as a microscopic glass disk that has whispering-gallery modes). This kind of structure naturally has a series of resonant modes with approximately equally spaced frequencies (similar to a Fabry–Pérot interferometer). Unfortunately the resonant modes are not exactly equally spaced due to dispersion. Nevertheless, the four-wave mixing effect above can create and stabilize a perfect frequency comb in such a structure.[9] Basically, the system generates a perfect comb that overlaps the resonant modes as much as possible. In fact, nonlinear effects can shift the resonant modes to improve the overlap with the perfect comb even more. (The resonant mode frequencies depend on refractive index, which is altered by the optical Kerr effect.)
In the time domain, while mode-locked lasers almost always emit a series of short pulses, Kerr frequency combs generally do not.[10] However, a special sub-type of Kerr frequency comb, in which a "cavity soliton" forms in the microresonator, does emit a series of pulses.[11]
Using electro-optic modulation of a continuous-wave laser
An optical frequency comb can be generated by modulating the amplitude and/or phase of a continuous-wave laser with an external modulator driven by a radio-frequency source.[12] In this manner, the frequency comb is centered around the optical frequency provided by the continuous-wave laser and the modulation frequency or repetition rate is given by the external radio-frequency source. The advantage of this method is that it can reach much higher repetition rates (>10 GHz) than with mode-locked lasers and the two degrees of freedom of the comb can be set independently.[13] The number of lines is lower than with a mode-locked laser (typically a few tens), but the bandwidth can be significantly broadened with nonlinear fibers.[14] This type of optical frequency comb is usually called electrooptic frequency comb.[15] The first schemes used a phase modulator inside an integrated Fabry–Perot cavity,[16] but with advances in electro-optic modulators new arrangements are possible.
Low-frequency combs using electronics
A purely electronic device which generates a series of pulses, also generates a frequency comb. These are produced for electronic sampling oscilloscopes, but also used for frequency comparison of microwaves, because they reach up to 1 THz. Since they include 0 Hz, they do not need the tricks which make up the rest of this article.
Widening to one octave
For many applications, the comb must be widened to at least an octave:[citation needed] that is, the highest frequency in the spectrum must be at least twice the lowest frequency. One of three techniques may be used:
- supercontinuum generation by strong self-phase modulation in nonlinear photonic crystal fiber or integrated waveguide
- a Ti:sapphire laser using intracavity self-phase modulation
- the second harmonic can be generated in a long crystal so that by consecutive sum frequency generation and difference frequency generation the spectrum of first and second harmonic widens until they overlap.
These processes generate new frequencies on the same comb for similar reasons as discussed above.
Carrier–envelope offset measurement

An increasing offset between the optical phase and the maximum of the wave envelope of an optical pulse can be seen on the right. Each line is displaced from a harmonic of the repetition rate by the carrier–envelope offset frequency. The carrier–envelope offset frequency is the rate at which the peak of the carrier frequency slips from the peak of the pulse envelope on a pulse-to-pulse basis.
Measurement of the carrier–envelope offset frequency is usually done with a self-referencing technique, in which the phase of one part of the spectrum is compared to its harmonic. Different possible approaches for carrier–envelope offset phase control were proposed in 1999.[17] The two simplest approaches, which require only one nonlinear optical process, are described in the following.
In the "f − 2f" technique, light at the lower-energy side of the broadened spectrum is doubled using second-harmonic generation (SHG) in a nonlinear crystal, and a heterodyne beat is generated between that and light at the same wavelength on the upper-energy side of the spectrum. This beat signal, detectable with a photodiode,[18] includes a difference-frequency component, which is the carrier–envelope offset frequency.
Conceptually, light at frequency is doubled to , and mixed with light at the very similar frequency to produces a beat signal at frequency In practice, this is not done with a single frequency but with a range of values, but the effect is the same
Alternatively, difference-frequency generation (DFG) can be used. From light at opposite ends of the broadened spectrum the difference frequency is generated in a nonlinear crystal, and a heterodyne beat between this mixing product and light at the same wavelength of the original spectrum is measured. This beat frequency, detectable with a photodiode, is the carrier–envelope offset frequency.
Here, light at frequencies and is mixed to produce light at frequency . This is then mixed with light at frequency to produce a beat frequency of This avoids the need for frequency doubling at the cost of a second optical mixing step. Again, practical implementation uses a range of values, not a single one.
Because the phase is measured directly, and not the frequency, it is possible to set the frequency to zero and additionally lock the phase, but because the intensity of the laser and this detector is not very stable, and because the whole spectrum beats in phase,[19] one has to lock the phase on a fraction of the repetition rate.
Carrier–envelope offset control
In the absence of active stabilization, the repetition rate and carrier–envelope offset frequency would be free to drift. They vary with changes in the cavity length, refractive index of laser optics, and nonlinear effects such as the Kerr effect. The repetition rate can be stabilized using a piezoelectric transducer, which moves a mirror to change the cavity length.
In Ti:sapphire lasers using prisms for dispersion control, the carrier–envelope offset frequency can be controlled by tilting the high reflector mirror at the end of the prism pair. This can be done using piezoelectric transducers.
In high repetition rate Ti:sapphire ring lasers, which often use double-chirped mirrors to control dispersion, modulation of the pump power using an acousto-optic modulator is often used to control the offset frequency. The phase slip depends strongly on the Kerr effect, and by changing the pump power one changes the peak intensity of the laser pulse and thus the size of the Kerr phase shift. This shift is far smaller than 6 rad, so an additional device for coarse adjustment is needed. A pair of wedges, one moving in or out of the intra-cavity laser beam can be used for this purpose.
The breakthrough which led to a practical frequency comb was the development of technology for stabilizing the carrier–envelope offset frequency.
An alternative to stabilizing the carrier–envelope offset frequency is to cancel it completely by use of difference frequency generation (DFG). If the difference frequency of light of opposite ends of a broadened spectrum is generated in a nonlinear crystal, the resulting frequency comb is carrier–envelope offset-free since the two spectral parts contributing to the DFG share the same carrier–envelope offset frequency (CEO frequency). This was first proposed in 1999 [17] and demonstrated in 2011 using an erbium fiber frequency comb at the telecom wavelength.[20] This simple approach has the advantage that no electronic feedback loop is needed as in conventional stabilization techniques. It promises to be more robust and stable against environmental perturbations.[21][22]
Applications

A frequency comb allows a direct link from radio frequency standards to optical frequencies. Current frequency standards such as atomic clocks operate in the microwave region of the spectrum, and the frequency comb brings the accuracy of such clocks into the optical part of the electromagnetic spectrum. A simple electronic feedback loop can lock the repetition rate to a frequency standard.
There are two distinct applications of this technique. One is the optical clock, where an optical frequency is overlapped with a single tooth of the comb on a photodiode, and a radio frequency is compared to the beat signal, the repetition rate, and the CEO-frequency (carrier–envelope offset). Applications for the frequency-comb technique include optical metrology, frequency-chain generation, optical atomic clocks, high-precision spectroscopy, and more precise GPS technology.[24]
The other is doing experiments with few-cycle pulses, like above-threshold ionization, attosecond pulses, highly efficient nonlinear optics or high-harmonics generation. These can be single pulses, so that no comb exists, and therefore it is not possible to define a carrier–envelope offset frequency, rather the carrier–envelope offset phase is important. A second photodiode can be added to the setup to gather phase and amplitude in a single shot, or difference-frequency generation can be used to even lock the offset on a single-shot basis, albeit with low power efficiency.
Without an actual comb one can look at the phase vs frequency. Without a carrier–envelope offset all frequencies are cosines. This means that all frequencies have the phase zero. The time origin is arbitrary. If a pulse comes at later times, the phase increases linearly with frequency, but still the zero-frequency phase is zero. This phase at zero frequency is the carrier–envelope offset. The second harmonic not only has twice the frequency, but also twice the phase. Thus for a pulse with zero offset the second harmonic of the low-frequency tail is in phase with the fundamental of the high-frequency tail, and otherwise it is not. Spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction (SPIDER) measures how the phase increases with frequency, but it cannot determine the offset, so the name “electric field reconstruction” is a bit misleading.
In recent years, the frequency comb has been garnering interest for astro-comb applications, extending the use of the technique as a spectrographic observational tool in astronomy.
There are other applications that do not need to lock the carrier–envelope offset frequency to a radio-frequency signal.[25] These include, among others, optical communications,[26] the synthesis of optical arbitrary waveforms,[27] spectroscopy (especially dual-comb spectroscopy)[28] or radio-frequency photonics.[13]
On the other hand, optical frequency combs have found new applications in remote sensing. Ranging lidars based on dual comb spectroscopy have been developed, enabling high-resolution range measurements at fast update rates.[29] Optical frequency combs can also be utilized to measure greenhouse gas emissions with great precision. For instance, in 2019, scientists at NIST employed spectroscopy to quantify methane emissions from oil and gas fields [30]. More recently, a greenhouse gas lidar based on electro-optic combs has been successfully demonstrated.[31]
History
The frequency comb was proposed in 2000. Before its introduction, the EM spectrum was divided between the electronic/radio frequency range and the optical/laser frequency range. The radio frequency range had accurate frequency counters, allowing highly accurate measurements of absolute frequency. The optical range has no such device. The two ranges are separated by a frequency gap of .
Before the frequency comb, the only way to bridge the gap were the harmonic frequency chains, which doubles radio frequency in 15 stages, reaching a frequency multiplication of . However, those were large and expensive to operate. The frequency comb managed to bridge that gap in one stage.[32]
Theodor W. Hänsch and John L. Hall shared half of the 2005 Nobel Prize in Physics for contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency-comb technique. The other half of the prize was awarded to Roy Glauber.
Also in 2005, the femtosecond comb technique was extended to the extreme ultraviolet range, enabling frequency metrology in that region of the spectrum.[33][34][35][36]
See also
References
- ^ Hall, John L. (2006). "Nobel Lecture: Defining and measuring optical frequencies". Reviews of Modern Physics. 78 (4): 1279–1295. Bibcode:2006RvMP...78.1279H. doi:10.1103/revmodphys.78.1279.
- ^ Hänsch, Theodor W. (2006). "Nobel Lecture: Passion for precision". Reviews of Modern Physics. 78 (4): 1297–1309. Bibcode:2006RvMP...78.1297H. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.208.7371. doi:10.1103/revmodphys.78.1297.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 2005". www.nobelprize.org. Retrieved 2017-11-16.
- ^ Adler, Florian; Moutzouris, Konstantinos; Leitenstorfer, Alfred; Schnatz, Harald; Lipphardt, Burghard; Grosche, Gesine; Tauser, Florian (2004-11-29). "Phase-locked two-branch erbium-doped fiber laser system for long-term precision measurements of optical frequencies". Optics Express. 12 (24): 5872–80. Bibcode:2004OExpr..12.5872A. doi:10.1364/OPEX.12.005872. ISSN 1094-4087. PMID 19488226.
- ^ Ma, Long-Sheng; Bi, Zhiyi; Bartels, Albrecht; et al. (2004). "Optical Frequency Synthesis and Comparison with Uncertainty at the 10−19 Level" (PDF). Science. 303 (5665): 1843–1845. Bibcode:2004Sci...303.1843M. doi:10.1126/science.1095092. PMID 15031498. S2CID 15978159.
- ^ Bartels, Albrecht (14 July 2009). "10-GHz Self-Referenced Optical Frequency Comb". Science. 326 (5953): 681. Bibcode:2009Sci...326..681B. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.668.1986. doi:10.1126/science.1179112. PMID 19900924. S2CID 30199867.
- ^ Boggio, J. C.; Moro, S.; Windmiller, J. R.; Zlatanovic, S.; Myslivets, E.; Alic, N.; Radic, S. (2009). "Optical frequency comb generated by four-wave mixing in highly nonlinear fibers". Cleo/Qels 2009: 1–2.
- ^ Sefler, G.A.; Kitayama, K. (1998). "Frequency comb generation by four-wave mixing and the role of fiber dispersion". Journal of Lightwave Technology. 16 (9): 1596–1605. Bibcode:1998JLwT...16.1596S. doi:10.1109/50.712242.
- ^ P. Del'Haye; A. Schliesser; O. Arcizet; T. Wilken; R. Holzwarth; T. J. Kippenberg (2007). "Optical frequency comb generation from a monolithic microresonator". Nature. 450 (7173): 1214–1217. arXiv:0708.0611. Bibcode:2007Natur.450.1214D. doi:10.1038/nature06401. PMID 18097405. S2CID 4426096.
- ^ Jérôme Faist; et al. (2016). "Quantum Cascade Laser Frequency Combs". Nanophotonics. 5 (2): 272. arXiv:1510.09075. Bibcode:2016Nanop...5...15F. doi:10.1515/nanoph-2016-0015. S2CID 119189132. "In contrast to mode-locked lasers, microresonator-based frequency combs (also called Kerr combs) can exhibit complex phase relations between modes that do not correspond to the emission of single pulses while remaining highly coherent [8]."
- ^ Andrew M. Weiner (2017). "Frequency combs: Cavity solitons come of age". Nature Photonics. 11 (9): 533–535. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2017.149. S2CID 126121332.
- ^ Murata, H.; Morimoto, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamamoto, S. (2000-11-01). "Optical pulse generation by electrooptic-modulation method and its application to integrated ultrashort pulse generators". IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics. 6 (6): 1325–1331. Bibcode:2000IJSTQ...6.1325M. doi:10.1109/2944.902186. ISSN 1077-260X. S2CID 41791989.
- ^ a b Torres-Company, Victor; Weiner, Andrew M. (May 2017). "Optical frequency comb technology for ultra-broadband radio-frequency photonics". Laser & Photonics Reviews. 8 (3): 368–393. arXiv:1403.2776. doi:10.1002/lpor.201300126. S2CID 33427587.
- ^ Wu, Rui; Torres-Company, Victor; Leaird, Daniel E.; Weiner, Andrew M. (2013-03-11). "Supercontinuum-based 10-GHz flat-topped optical frequency comb generation". Optics Express. 21 (5): 6045–6052. Bibcode:2013OExpr..21.6045W. doi:10.1364/OE.21.006045. ISSN 1094-4087. PMID 23482172.
- ^ Metcalf, A. J.; Torres-Company, V.; Leaird, D. E.; Weiner, A. M. (2013-11-01). "High-Power Broadly Tunable Electrooptic Frequency Comb Generator". IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics. 19 (6): 231–236. Bibcode:2013IJSTQ..19..231M. doi:10.1109/JSTQE.2013.2268384. ISSN 1077-260X. S2CID 37911312.
- ^ Kobayashi, T.; Sueta, T.; Cho, Y.; Matsuo, Y. (1972-10-15). "High-repetition-rate optical pulse generator using a Fabry-Perot electro-optic modulator". Applied Physics Letters. 21 (8): 341–343. Bibcode:1972ApPhL..21..341K. doi:10.1063/1.1654403. ISSN 0003-6951.
- ^ a b Telle, H. R.; Steinmeyer, G.; Dunlop, A. E.; Stenger, J.; Sutter, D. H.; Keller, U. (October 1999). "Carrier–envelope offset phase control: A novel concept for absolute optical frequency measurement and ultrashort pulse generation" (PDF). Appl. Phys. B. 69 (4): 327–332. doi:10.1007/s003400050813.
- ^ Hu, Yue; et al. (15 March 2017). "Computational Study of Amplitude-to-Phase Conversion in a Modified Unitraveling Carrier Photodetector" (PDF). IEEE Photonics Journal. 9 (2) 2682251. arXiv:1702.07732. Bibcode:2017IPhoJ...982251H. doi:10.1109/JPHOT.2017.2682251. S2CID 19450831.
- ^ Rauschenberger, Jens (24 April 2007). Phase-stabilized Ultrashort Laser Systems for Spectroscopy (PDF) (PhD thesis). Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. doi:10.5282/edoc.7110. Retrieved 7 July 2024.
- ^ G. Krauss, D. Fehrenbacher, D. Brida, C. Riek, A. Sell, R. Huber, A. Leitenstorfer (2011). "All-passive phase locking of a compact Er:fiber laser system", Opt. Lett., 36, 540.
- ^ T. Fuji, A. Apolonski, F. Krausz (2004). "Self-stabilization of carrier–envelope offset phase by use of difference-frequency generation", Opt. Lett., 29, 632.
- ^ M. Zimmermann, C. Gohle, R. Holzwarth, T. Udem, T.W. Hänsch (2004). "Optical clockwork with an offset-free difference-frequency comb: accuracy of sum- and difference-frequency generation", Opt. Lett., 29, 310.
- ^ "HARPS Laser Frequency Comb Commissioned". European Southern Observatory. 22 May 2015.
- ^ Optical frequency comb for dimensional metrology, atomic and molecular spectroscopy, and precise time keeping Archived 2013-06-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Newbury, Nathan R. (2011). "Searching for applications with a fine-tooth comb". Nature Photonics. 5 (4): 186–188. Bibcode:2011NaPho...5..186N. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2011.38.
- ^ Temprana, E.; Myslivets, E.; Kuo, B. P.-P.; Liu, L.; Ataie, V.; Alic, N.; Radic, S. (2015-06-26). "Overcoming Kerr-induced capacity limit in optical fiber transmission". Science. 348 (6242): 1445–1448. Bibcode:2015Sci...348.1445T. doi:10.1126/science.aab1781. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 26113716. S2CID 41906650.
- ^ Cundiff, Steven T.; Weiner, Andrew M. (2010). "Optical arbitrary waveform generation". Nature Photonics. 4 (11): 760–766. Bibcode:2010NaPho...4..760C. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2010.196.
- ^ Coddington, Ian; Newbury, Nathan; Swann, William (2016-04-20). "Dual-comb spectroscopy". Optica. 3 (4): 414–426. Bibcode:2016Optic...3..414C. doi:10.1364/OPTICA.3.000414. ISSN 2334-2536. PMC 8201420. PMID 34131580.
- ^ Nürnberg, Jacob; Willenberg, Benjamin; Phillips, Christopher R.; Keller, Ursula (2021-08-02). "Dual-comb ranging with frequency combs from single cavity free-running laser oscillators". Optics Express. 29 (16): 24910. Bibcode:2021OExpr..2924910N. doi:10.1364/OE.428051. ISSN 1094-4087. PMID 34614835.
- ^ robin.materese@nist.gov (2009-12-31). "Optical Frequency Combs". NIST. Retrieved 2022-02-16.
- ^ Patiño Rosas, William; Cézard, Nicolas (2024). "Greenhouse gas monitoring using an IPDA lidar based on a dual-comb spectrometer". Optics Express. 32 (8): 13614. Bibcode:2024OExpr..3213614P. doi:10.1364/oe.515543. PMID 38859327. Retrieved 2024-04-02.
- ^ Diddams, Scott A.; Vahala, Kerry; Udem, Thomas (2020-07-17). "Optical frequency combs: Coherently uniting the electromagnetic spectrum". Science. 369 (6501): 367. Bibcode:2020Sci...369..367D. doi:10.1126/science.aay3676. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 32675346.
- ^ Jones, R. Jason; Moll, Kevin D.; Thorpe, Michael J.; Ye, Jun (20 May 2005), "Phase-Coherent Frequency Combs in the Vacuum Ultraviolet via High-Harmonic Generation inside a Femtosecond Enhancement Cavity" (PDF), Physical Review Letters, 94 (19): 193201, Bibcode:2005PhRvL..94s3201J, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.193201, PMID 16090171, archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-12, retrieved 2014-07-31
- ^ Gohle, Christoph; Udem, Thomas; Herrmann, Maximilian; Rauschenberger, Jens; Holzwarth, Ronald; Schuessler, Hans A.; Krausz, Ferenc; Hänsch, Theodor W. (2005), "A frequency comb in the extreme ultraviolet", Nature, 436 (14 July 2005): 234–237, Bibcode:2005Natur.436..234G, doi:10.1038/nature03851, PMID 16015324, S2CID 1029631
- ^ Kandula, Dominik Z.; Gohle, Christoph; Pinkert, Tjeerd J.; Ubachs, Wim; Eikema, Kjeld S.E. (2 August 2010). "Extreme ultraviolet frequency comb metrology". Physical Review Letters. 105 (6): 063001. arXiv:1004.5110. Bibcode:2010PhRvL.105f3001K. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.063001. PMID 20867977. S2CID 2499460.
- ^ Cingöz, Arman; Yost, Dylan C.; Allison, Thomas K.; Ruehl, Axel; Fermann, Martin E.; Hartl, Ingmar; Ye, Jun (2 February 2012), "Direct frequency comb spectroscopy in the extreme ultraviolet", Nature, 482 (7383): 68–71, arXiv:1109.1871, Bibcode:2012Natur.482...68C, doi:10.1038/nature10711, PMID 22297971, S2CID 1630174
Further reading
- Nathalie Picqué; Theodor Hänsch (2019). "Frequency comb spectroscopy". Nature Photonics. 13 (3): 146–157. arXiv:1902.11249. Bibcode:2019NaPho..13..146P. doi:10.1038/s41566-018-0347-5. S2CID 119189885.
- Steven T. Cundiff; Jun Ye (2003). "Colloquium: Femtosecond optical frequency combs". Reviews of Modern Physics. 75 (1): 325. Bibcode:2003RvMP...75..325C. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.152.1154. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.75.325.
- John L Hall & Theodor W Hänsch (2004). "History of optical comb development" (PDF). In Jun Ye, Steven T Cundiff (ed.). Femtosecond optical frequency comb. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-23790-9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-12-27. Retrieved 2013-01-20.
- Andrew M. Weiner (2009). Ultrafast Optics. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-41539-8.
- Nobel prize for Physics (2005) Press Release
External links
- Attosecond control of optical waveforms
- Femtosecond laser comb
- Optical frequency comb for dimensional metrology, atomic and molecular spectroscopy, and precise time keeping
- Rulers of Light: Using Lasers to Measure Distance and Time by Steven Cundiff in Scientific American
- On-chip, electronically tunable frequency comb, article by Leah Burrows | March 18, 2019
- Optical Frequency Combs explanation by NIST


















