DVB

| List of digital television broadcast standards |
|---|
| DVB standards (countries) |
| ATSC standards (countries) |
|
| ISDB standards (countries) |
| DTMB standards (countries) |
| DMB standard (countries) |
| Codecs |
|
| Terrestrial Frequency bands |
| Satellite Frequency bands |
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium,[1] and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU).
Transmission
DVB systems distribute data using a variety of approaches, including:
- Satellite: DVB-S, DVB-DSNG, DVB-S2, DVB-S2X and DVB-SH
- Cable: DVB-C, DVB-C2
- Terrestrial television: DVB-T, DVB-T2
- Microwave: using DTT (DVB-MT), the MMDS (DVB-MC), and/or MVDS standards (DVB-MS)
These standards define the physical layer and data link layer of the distribution system. Devices interact with the physical layer via a synchronous parallel interface (SPI), synchronous serial interface (SSI) or asynchronous serial interface (ASI). All data is transmitted in MPEG transport streams with some additional constraints (DVB-MPEG). A standard for temporally-compressed distribution to mobile devices (DVB-H) was published in November 2004.
These distribution systems differ mainly in the modulation schemes used and error correcting codes used, due to the different technical constraints. DVB-S (SHF) uses QPSK, 8-PSK or 16-QAM. DVB-S2 uses QPSK, 8-PSK, 16-APSK or 32-APSK, at the broadcasters decision. QPSK and 8-PSK are the only versions regularly used. DVB-C (VHF/UHF) uses QAM: 16-QAM, 32-QAM, 64-QAM, 128-QAM or 256-QAM. Lastly, DVB-T (VHF/UHF) uses 16-QAM or 64-QAM (or QPSK) in combination with (C)OFDM and can support hierarchical modulation.
The DVB-T2 specification was approved by the DVB Steering Board in June 2008 and sent to ETSI for adoption as a formal standard. ETSI adopted the standard on 9 September 2009.[2] The DVB-T2 standard gives more robust TV reception and increases the possible bit rate by over 30% for single transmitters (as in the UK) and will increase the maximum bit rate by over 50% in large single-frequency networks (as in Germany and Sweden).
DVB has established a 3D TV group (CM-3DTV) to identify "what kind of 3D-TV solution does the market want and need, and how can DVB play an active part in the creation of that solution?" The CM-3DTV group held a DVB 3D-TV Kick-off Workshop in Geneva on 25 January 2010, followed by the first CM-3DTV meeting the next day.[3] DVB now defines a new standard for 3D video broadcast: DVB 3D-TV.
Modes and features of latest DVB-x2 system standards in comparison:
| DVB-S2 | DVB-T2 | DVB-C2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input interface | Multiple transport stream and generic stream encapsulation (GSE) | Multiple transport stream and generic stream encapsulation (GSE) | Multiple transport stream and generic stream encapsulation (GSE) |
| Modes | Variable coding & modulation and adaptive coding & modulation | Variable coding & modulation[4] | Variable coding & modulation and adaptive coding & modulation |
| FEC | LDPC + BCH 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10 | LDPC + BCH 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6 | LDPC + BCH 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10[5] |
| Modulation | Single carrier, PSK or APSK, multiple streams | OFDM | absolute OFDM[6] |
| Modulation schemes | QPSK, 8-PSK, 16-APSK, 32-APSK | QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM, 256-QAM | 16- to 4096-QAM |
| Guard interval | Not applicable | 1/4, 19/256, 1/8, 19/128, 1/16, 1/32, 1/128 | 1/64 or 1/128 |
| Fourier transform size | Not applicable | 1k, 2k, 4k, 8k, 16k, 32k DFT | 4k Inverse FFT[7] |
| Interleaving | Bit-Interleaving | Bit- time- and frequency-interleaving | Bit- time- and frequency-interleaving |
| Pilots | Pilot symbols | Scattered and continual pilots | Scattered and continual pilots |
Content
Digital video content is encoded using discrete cosine transform (DCT) based video coding standards, such as the H.26x and MPEG formats. Digital audio content is encoded using modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) based audio coding standards, such as Advanced Audio Coding (AAC), Dolby Digital (AC-3) and MP3.
Besides digital audio and digital video transmission, DVB also defines data connections (DVB-DATA - EN 301 192) with return channels (DVB-RC) for several media (DECT, GSM, PSTN/ISDN, satellite etc.) and protocols (DVB-IPTV: Internet Protocol; DVB-NPI: network protocol independent).
Older technologies such as teletext (DVB-TXT) and vertical blanking interval data (DVB-VBI) are also supported by the standards to ease conversion. However, for many applications more advanced alternatives like DVB-SUB for subtitling are available.
Encryption and metadata
The conditional access system (DVB-CA) defines a Common Scrambling Algorithm (DVB-CSA) and a physical Common Interface (DVB-CI) for accessing scrambled content. DVB-CA providers develop their wholly proprietary conditional access systems with reference to these specifications. Multiple simultaneous CA systems can be assigned to a scrambled DVB program stream providing operational and commercial flexibility for the service provider.
The DVB Project developed a Content Protection and Copy Management system for protecting content after it has been received (DVB-CPCM), which was intended to allow flexible use of recorded content on a home network or beyond, while preventing unconstrained sharing on the Internet. DVB-CPCM was the source of much controversy in the popular press and it was said that CPCM was the DVB Project's answer to the failed American Broadcast Flag.[8] The DVB-CPCM specifications, which were standardized by ETSI as a multipart document (TS 102 825) between 2008 and 2013,[9] were deprecated by the DVB Steering Board in February 2019.
DVB transports include metadata called Service Information (DVB-SI, ETSI EN 300 468, ETSI TR 101 211) that links the various elementary streams into coherent programs and provides human-readable descriptions for electronic program guides as well as for automatic searching and filtering. The dating system used with this metadata suffers from a year 2038 problem in which due to the limited 16 bits and modified Julian day offset used will cause an overflow issue similar to the year 2000 problem. By comparison, the rival DigiCipher 2 based ATSC system will not have this issue until 2048 due in part to 32 bits being used.[citation needed]
DVB adopted a profile of the metadata defined by the TV-Anytime Forum (DVB-TVA, ETSI TS 102323). This is an XML Schema based technology and the DVB profile is tailored for enhanced Personal Digital Recorders.
In the early 2000s, DVB started an activity to develop specifications for IPTV (DVB-IPI, ETSI TR 102 033, ETSI TS 102 034, ETSI TS 102 814), which also included metadata definitions for a broadband content guide (DVB-BCG, ETSI TS 102 539).
DVB-I
In October 2017, the DVB Project established a working group to begin the definition of a specification for "standalone TV services over IP, referred to as DVB-I services".[10] Work on the commercial requirements for DVB-I began in January 2018 and the terms of reference were agreed in March 2018.[11]
The DVB-I specification, titled "Service Discovery and Programme Metadata for DVB-I", was approved by the DVB Project in November 2019[12] [13] and first published as DVB BlueBook A177 in June 2020[14] and as an ETSI standard TS 103 770 in November 2020.[15]
The DVB-I specification defines ways in which devices and displays connected to the internet can discover and access sets of audiovisual media services. These can include services delivered online through fixed and wireless Internet Protocol connections as well as broadcast radio and television channels received over radio frequency networks using traditional cable, satellite, or terrestrial transmissions.
Tests and pilots of DVB-I services have been undertaken in several countries including Iran, Germany, Italy, Spain and Ireland.[16]
Software platform
The DVB Multimedia Home Platform (DVB-MHP) defines a Java-based platform for the development of consumer video system applications. In addition to providing abstractions for many DVB and MPEG-2 concepts, it provides interfaces for other features like network card control, application download, and layered graphics.
Return channel
DVB has standardized a number of return channels that work together with DVB(-S/T/C) to create bi-directional communication. RCS is short for Return Channel Satellite, and specifies return channels in C, Ku and Ka frequency bands with return bandwidth of up to 2 Mbit/s. DVB-RCT is short for Return Channel Terrestrial, specified by ETSI EN 301958.
Service discovery
The DVB-I standard (ETSI TS 103 770) defines an internet-based request and response mechanism to discover and access audiovisual services delivered over traditional digital broadcast transmissions or Internet Protocol networks and present them in a unified way.[17]
Adoption
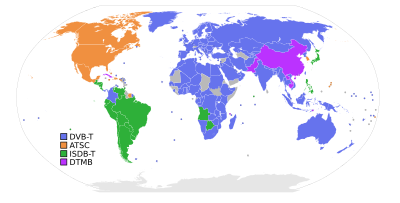
DVB-S and DVB-C were ratified in 1994. DVB-T was ratified in early 1997. The first commercial DVB-T broadcasts were performed by the United Kingdom's Digital TV Group in late 1998. In 2003 Berlin, Germany was the first area to completely stop broadcasting analogue TV signals. Most European countries are fully covered by digital television and many have switched off PAL/SECAM services.
DVB standards are used throughout Europe, as well as in Australia, South Africa and India. They are also used for cable and satellite broadcasting in most Asian, African and many South American countries. Some have chosen ISDB-T instead of DVB-T and a few (United States, Canada, Mexico and South Korea) have chosen ATSC instead of DVB-T.
Africa
Kenya
DVB-T broadcasts were launched by the President of Kenya, Mwai Kibaki on 9 December 2009. Broadcasts are using H.264, with the University of Nairobi supplying the decoders. Kenya has also been broadcasting DVB-H since July 2009, available on selected Nokia and ZTE handsets on the Safaricom and other GSM networks.[18]
Madagascar
Since 2011, the pay TV operator Blueline[19] launched a DVB-T service branded BluelineTV.[20] It supplies both smart cards and set-top-boxes.
South Africa
Since 1995, the pay TV operator DStv used the DVB-S standard to broadcast its services. In 2010, it started a DVB over IP service, and in 2011 it started DStv mobile using the DVB-H standard.[21]
In late 2010, the South African cabinet endorsed a decision by a Southern African Development Community (SADC) task team to adopt the DVB-T2 standard.[22]
Asia
Hong Kong
In Hong Kong, several cable TV operators such as TVB Pay Vision and Cable TV have already started using DVB-S or DVB-C. The government however has adopted the DMB-T/H standard, developed in mainland China, for its digital terrestrial broadcasting services which has started since 31 December 2007.[23]
Iran
On 17 March 2009, DVB-H and DVB-T H.264/AAC broadcasting started in Tehran by the IRIB. DVB-T broadcasting is now widely available in other cities such as Isfahan, Mashhad, Shiraz, Qom, Tabriz and Rasht as well.
Israel
DVB-T broadcasts using H.264 commenced in Israel on 1 June 2009 with the broadcast trial and the full broadcast began on 2 August 2009. Analog broadcasts were originally planned to end in 18 months after the launch, but analog broadcasts were switched off on 31 March 2011 instead.
During 2010, DVB-T broadcasts have become widely available in most of Israel and an EPG was added to the broadcasts.[24]
Japan
With the exception of SKY PerfecTV!, Japan uses different formats in all areas (ISDB), which are however quite similar to their DVB counterparts. SkyPerfect is a satellite provider using DVB on its 124 and 128 degrees east satellites. Its satellite at 110 degrees east does not use DVB, however.
Malaysia
In Malaysia, a new pay television station MiTV began service in September 2005 using DVB-IPTV technology while lone satellite programming provider ASTRO has been transmitting in DVB-S since its inception in 1996. Free-to-air DVB-T trials began in late 2006 with a simulcast of both TV1 and TV2 plus a new channel called RTM3/RTMi. In April 2007, RTM announced that the outcome of the test was favourable and that it expected DVB-T to go public by the end of 2007. However, the system did not go public as planned. As of 2008, the trial digital line-up has expanded to include a music television channel called Muzik Aktif, and a sports channel called Arena, with a news channel called Berita Aktif planned for inclusion in the extended trials soon. Also, high definition trials were performed during the Beijing Olympics and the outcome was also favourable. It was announced that the system would go public in 2009.
In 2009, MiTV closed down, changed its name to U-Television and announced that it was changing to scrambled DVB-T upon relaunch instead of the DVB-IPTV system used prior to shutting down. However, RTM's digital network again did not go public, although around this time TVs that are first-generation DVB-T capable went on sale. The government has since announced that they will be deploying DVB-T2 instead in stages starting in mid-2015 and analog shutoff has been delayed to April 2019.
Philippines
In the Philippines, DVB-S and DVB-S2 are the two broadcast standards currently used by satellite companies, while DVB-C is also used by some cable companies. The government adopted DVB-T in November 2006 for digital terrestrial broadcasting but a year later, it considered other standards to replace DVB-T. The country has chosen the ISDB-T system instead of DVB-T.
Taiwan
In Taiwan, some digital cable television systems use DVB-C, though most customers still use analogue NTSC cable television. The government planned adopting ATSC or the Japanese ISDB-T standard as NTSC's replacement. However, the country has chosen the European DVB-T system instead. Public Television Service (PTS) and Formosan TV provide high definition television. The former has the channel HiHD; the latter uses its HD channel for broadcasting MLB baseball.
Europe
Cyprus
Cyprus uses DVB-T with MPEG-4 encoding. Analogue transmission stopped on 1 July 2011 for all channels except CyBC 1.
Denmark
In Denmark, DVB-T replaced the analog transmission system for TV on 1 November 2009. Danish national digital TV transmission has been outsourced to the company Boxer TV A/S,[25] acting as gatekeeper organization for terrestrial TV transmission in Denmark.[26][27] However, there are still several free channels from DR.
Finland
DVB-T transmissions were launched on 21 August 2001. The analogue networks continued alongside the digital ones until 1 September 2007, when they were shut down nationwide. Before the analogue switchoff, the terrestrial network had three multiplexes: MUX A, MUX B and MUX C. MUX A contained the channels of the public broadcaster Yleisradio and MUX B was shared between the two commercial broadcasters: MTV3 and Nelonen. MUX C contained channels of various other broadcasters. After the analogue closedown, a fourth multiplex named MUX E was launched. All of the Yleisradio (YLE) channels are broadcast free-to-air, likewise a handful of commercial ones including MTV3, Nelonen, Subtv, Jim, Nelonen Sport, Liv, FOX, TV5 Finland, AVA and Kutonen. There are also several pay channels sold by PlusTV.
Italy
In Italy, DVB-S started in 1996 and the final analogue broadcasts were terminated in 2005. The switch-off from analogue terrestrial network to DVB-T started on 15 October 2008. Analogue broadcast was ended on 4 July 2012 after nearly four years of transition in phases.
Netherlands
In the Netherlands, DVB-S broadcasting started on 1 July 1996, satellite provider MultiChoice (now CanalDigitaal) switched off the analogue service shortly after on 18 August 1996. DVB-T broadcasting started April 2003, and terrestrial analog broadcasting was switched off December 2006. It was initially marketed by Digitenne but later by KPN. Multiplex 1 contains the NPO 1, NPO 2 and NPO 3 national TV channels, and a regional channel. Multiplexes 2~5 have the other encrypted commercial and international channels. Multiplex 1 also broadcasts the radio channels Radio 1, Radio 2, 3 FM, Radio 4, Radio 5, Radio 6, Concertzender, FunX and also a regional channel. As of June 2011, the Dutch DVB-T service had 29 TV channels and 20 radio channels (including free to air channels). DVB-T2 will be introduced during 2019/2020.
Norway
In Norway, DVB-T broadcasting is marketed under RiksTV (encrypted pay channels) and NRK (unencrypted public channels). DVB-T broadcasting via the terrestrial network began in November 2007, and has subsequently been rolled out one part of the country at a time. The Norwegian implementation of DVB-T is different from most others, as it uses H.264 with HE-AAC audio encoding, while most other countries have adapted the less recent MPEG-2 standard. Notably most DVB software for PC has problems with this, though in late 2007 compatible software was released, like DVBViewer using the libfaad2 library. Sony has released several HDTVs (Bravia W3000, X3000, X3500, E4000, V4500, W4000, W4500, X4500) that support Norway's DVB-T implementation without use of a separate set-top box, and Sagem ITD91 HD, Grundig DTR 8720 STBs are others.
Poland
Currently, Poland uses the DVB-T2 standard with HEVC encoding. Analogue broadcast switch-off started on 7 November 2012 and was completed on 23 July 2013.[28]
Portugal
Portugal follows the DVB-T implementation, using H.264 with AAC audio encoding. It has been live since 29 April 2009 and the switch-off date for all analog signals was on 26 April 2012.
Romania
Romania started digital terrestrial broadcasting in 2005 but it was virtually unknown by many people in Romania due to the lack of content, cable TV and satellite TV being far more popular, however it was the first platform to deliver HD content. Today, Romania is using DVB-T2 as terrestrial standard, but also DVB-S/S2, and DVB-C which is extremely popular. The only analogue broadcast remains on cable. Romania adopted the DVB-T2 standard in 2016 after a series of tests with mpeg2, mpeg4 on DVB-T, and has today fully implemented DVB-T2. DVB-C, which was introduced in late 2005, still remains with mpeg2 on SD content and mpeg4 on HD content. DVB-S (introduced in 2004 focus sat being the first such platform) is used in basic packages with standard definition content, while DVB-S2 set top boxes are provided for both SD and HD content.
Russia
Fully switched to digital in 2019, Russia uses the DVB-T2 standard for broadcasting 2 channel packs with about ten main national radio and TV channels (Channel One, Rossiya 1/2/K/24, NTV, Radio Mayak, Radio Rossii etc.
Spain
Quiero TV started digital terrestrial broadcasting in 2000 as pay television. The platform closed three years later after gaining 200,000 subscribers. The frequencies used by Quiero TV were used from 2005 to simulcast free-to-air analogue broadcast as DVB-T, under the name "TDT". The service started with 20 free-to-air national TV channels as well as numerous regional and local channels. Analogue broadcast ended on 2010 after getting 100% digital coverage. Some of the analogue frequencies were used to increase the number of channels and simulcast some of them in HD. Since February 14th, 2024, all channels will be required to broadcast exclusively in HD. Frequencies of SD channels will be used to simulcast some of them in 4K using DVB-T2.
United Kingdom
In the UK DVB-T has been adopted for broadcast of standard definition terrestrial programming, as well as a single DVB-T2 multiplex for high-definition programming. The UK terminated all analogue terrestrial broadcasts by the end of 2012. The vast majority of channels are available free-to-air through the Freeview service. DVB-T was also used for the now-defunct ONDigital/ITV Digital and Top Up TV service.
All satellite programming (some of which is available free-to-air via Freesat or free-to-view via Freesat from Sky; the remainder requires a subscription to Sky), is broadcast using either DVB-S or DVB-S2.
Subscription-based cable television from Virgin Media uses DVB-C.
North America
In North America, DVB-S is often used in encoding and video compression of digital satellite communications alongside Hughes DSS. Unlike Motorola's DigiCipher 2 standard, DVB has a wider adoption in terms of the number of manufacturers of receivers. Terrestrial digital television broadcasts in Canada, Mexico, El Salvador, Honduras, and the United States use ATSC encoding with 8VSB modulation instead of DVB-T with COFDM. Television newsgathering links from mobile vans to central receive points (often on mountaintops or tall buildings) use DVB-T with COFDM in the 2 GHz frequency band.
Oceania
Australia
In Australia, DVB broadcasting is marketed under the Freeview brand name, and more recently 'Freeview Plus', denoting the integration of online HbbTV and EPG in certain DVB devices. Regular broadcasts began in January 2001 using MPEG 2 video and MPEG 1 audio[clarification needed] in SD and HD.
Changes to broadcasting rules have enabled broadcasters to offer multi-channeling, prompting broadcasters to use H.264 video with MPEG 1[clarification needed] or AAC audio encoding for some secondary channels.
Specifications for HD channels now differ depending on the broadcaster. ABC, Nine and Ten use 1920x1080i MPEG 4 video with Dolby Digital audio. Seven and SBS use 1440x1080i MPEG 2 video with Dolby Digital and MPEG 1 [clarification needed] respectively.[29]
New Zealand
In New Zealand, DVB broadcasting is marketed under the Freeview brand name. SD MPEG-2 DVB-S broadcasts via satellite began on 2 May 2007 and DVB-T (terrestrial) broadcasts began April 2008 broadcasting in HD H.264 video with HE-AAC audio.
South America
Colombia
Since 2008, Colombia has adopted as a public policy the decision to migrate from the analog television implemented in 1954 to Digital Terrestrial Television (DVB-T2). This measure allows the viewers access to the open television (OTA) of public and private channels, with video quality in HD. As planned, analogue television broadcasts will end in 2021.
DVB compliant products
Companies that manufacture a product which is compliant to one or more DVB standards have the option of registering a declaration of conformity for that product. Wherever the DVB trademark is used in relation to a product – be it a broadcast, a service, an application or equipment – the product must be registered with the DVB project office.[30]
Related standards
Other international standards for digital broadcasting and reception include ATSC, originally from the US, and ISDB, originally from Japan.
See also
- CI+ Common Interface Plus
- Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB)
- Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM, digital broadcasting over short and medium waves)
- Digital multimedia broadcasting (DMB)
- ETSI Satellite Digital Radio (SDR)
- FTA receiver
- ISDB – Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting
- DTMB – Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast, developed in China, also adopted by a few countries beyond
- List of digital television deployments by country
- WiB (digital terrestrial television)
References
- ^ "DVB - Digital Video Broadcasting". www.dvb.org. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "Work Programme: Details of 'DEN/JTC-DVB-228' Work Item Schedule". ETSI. Retrieved 29 August 2010.
- ^ "DVB - Digital Video Broadcasting - DVB 3D TV Kick-Off Workshop". Archived from the original on 15 January 2010. Retrieved 12 January 2010.
- ^ "Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Frame structure channel coding and modulation for a second generation digital terrestrial television broadcasting system (DVB-T2)" (PDF). DVB consortium. February 2011.
- ^ "Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Frame structure channel coding and modulation for a second generation digital transmission system for cable systems (DVB-C2)" (PDF). DVB consortium. 7 May 2010.
- ^ "Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Implementation Guidelines for a second generation digital cable transmission system (DVB-C2)" (PDF). DVB consortium. 19 November 2010.
- ^ "DVB-C2 The second generation transmission technology for broadband cable" (PDF). Dirk Jaeger, Philipp Hasse, Joerg Robert, Institut fuer Nachrichtentechnik at Technische Universitaet Braunschweig. 8 April 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 24 January 2013.
- ^ "Europe's Broadcast Flag". Electronic Frontier Foundation. 29 September 2005. Archived from the original on 13 October 2005. Retrieved 15 August 2007.
- ^ "ETSI Work Programme - Query Result of search for TS 102 825". etsi.org.
- ^ "Kicking Off DVB Internet TV Services" (PDF). DVB Scene (51): 6–7.
- ^ "DVB launches new DVB-I initiative for open internet". SVG Europe. 5 March 2018.
- ^ "DVB Approves Internet-Centric Linear TV DVB-I Specification". IBC.org. 13 November 2019.
- ^ "DVB approves new specification for linear TV delivered over the internet". TVB Europe. 13 November 2019.
- ^ Service Discovery and Programme Metadata for DVB-I: DVB Document A177 (PDF) (Rev.1 ed.). DVB. 2020.
- ^ ETSI TS 103 770 V1.1.1 (2020-11): Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Service Discovery and Programme Metadata for DVB-I (PDF). ETSI. 2020.
- ^ "DVB-I Deployments". DVB-I. 28 October 2024.
- ^ "Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB): Service Discovery and Programme Metadata for DVB-I" (PDF). ETSI. November 2020.
- ^ "Digital TV a reality in Kenya". Nation Media. Retrieved 9 December 2009.
- ^ "Blueline Madagascar". www.blueline.mg. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ BluelineTV
- ^ "The MultiChoice Group". 2 March 2023.
- ^ "SA to adopt European TV standard: report". 24.com. Retrieved 18 January 2011.
- ^ "Digital TV". www.digitaltv.gov.hk. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "About - DVB". www.dvb.org. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "Fleksible tv-pakker og bredbånd hos Boxer - Tv-udbyder med valgfrihed". www.boxertv.dk. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "Kulturministeriets hjemmeside" (PDF). www.kum.dk. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "Kulturministeriets hjemmeside". www.kum.dk. Archived from the original on 8 October 2009. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "General information about the digital broadcasting system in Poland". Ministry of Administration and Digitalization of Poland. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ^ "ABC HD is now live". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 27 December 2016.
- ^ Benoit, Herve. (2009). Digital Television : Satellite, Cable, Terrestrial, IPTV, Mobile TV in the DVB Framework. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-136-02714-7. OCLC 1024255874.
External links
