Bacan Islands
 Topographic map of Bacan and other nearby islands. | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 00°36′54″S 127°30′54″E / 0.61500°S 127.51500°E |
| Archipelago | Moluccas (Maluku Islands) |
| Area | 2,792.85 km2 (1,078.33 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,111 m (6926 ft) |
| Highest point | Buku Sibela |
| Administration | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 117,986 (mid 2023) |
| Pop. density | 42.2/km2 (109.3/sq mi) |

The Bacan Islands, formerly also known as the Bachans, Bachians, and Batchians,[1] are a group of islands in the Moluccas in Indonesia. They are mountainous and forested, lying south of Ternate and southwest of Halmahera. The islands are administered by the South Halmahera Regency of North Maluku Province. They formerly constituted the Sultanate of Bacan.
Bacan (Dutch: Batjan),[2] formerly also known as Bachian[3][2] or Batchian,[4] is the group's largest island. Bacan Island in 2020 included about 82,387 people, of whom 7,073 lived in the capital Labuha; it is subdivided into seven districts. The second and third-largest islands are Kasiruta and Mandioli.[3] Kasiruta and Mandioli each have over 11,000 inhabitants, and each is subdivided into two districts. A fourth island, Batang Lomang, forms a twelfth district within the group. There are dozens of smaller islands in the group, which had a total population of 84,075 at the 2010 Census,[5] but by the 2020 Census had risen to 111,517.[6] The official estimate as at mid 2023 was 117,986.[7]
Administration
The group is divided into twelve administrative districts (kecamatan) out of the thirty districts within South Halmahera Regency. They are tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census[5] and 2020 Census,[6] together with the official estimate for mid 2023.[7] The table also includes the number of administrative villages (all classed as rural desa) in each district and its post code.
| Kode Wilayah |
Name | English name | Area in km2 |
Popn census 2010 |
Popn census 2020 |
Popn estimate mid 2023 |
Admin. centre |
No. of villages |
No. of islands |
Post code |
Island or group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 82.04.21 | Bacan Timur Selatan | Southeast Bacan | 321.13 | 6,460 | 7,493 | 8,352 | Wayaua | 7 | 1 | 97791 | Bacan Island |
| 82.04.22 | Bacan Timur Tengah | East Central Bacan | 276.28 | 5,229 | 6,158 | 6,495 | Bibinoi | 7 | 2 | 97791 | Bacan Island |
| 82.04.07 | Bacan Timur | East Bacan | 463.50 | 9,051 | 12,794 | 13,649 | Babang | 10 | 8 | 97791 | Bacan Island |
| 82.04.17 | Bacan Selatan | South Bacan | 169.21 | 13,265 | 19,560 | 21,153 | Mandaong | 10 | - | 97791 | Bacan Island |
| 82.04.08 | Bacan | (Central Bacan) | 304.69 | 19,092 | 27,045 | 28,468 | Labuha | 14 | 3 | 97791 | Bacan Island |
| 82.04.14 | Bacan Barat Utara | Northwest Bacan | 264.94 | 4,096 | 5,010 | 5,099 | Yaba | 8 | 1 | 97791 | Bacan Island |
| 82.04.09 | Bacan Barat | West Bacan | 180.78 | 3,549 | 4,327 | 4,665 | Indari | 7 | 49 | 97791 | Bacan Island |
| 82.04.18 | Batang Lomang (a) | Batang Lomang Islands | 55.81 | 6,177 | 7,655 | 7,858 | Bajo | 8 | 13 | 97790 | Batang Lomang Islands |
| 82.04.19 | Mandioli Selatan | South Mandioli | 138.81 | 5,798 | 6,936 | 7,237 | Jiko | 6 | - | 97791 | Mandioli |
| 82.04.20 | Mandioli Utara | North Mandioli | 96.79 | 2,990 | 3,809 | 3,880 | Indong | 6 | 7 | 97791 (b) | Mandioli |
| 82.04.16 | Kasiruta Timur | East Kasiruta | 247.93 | 3,847 | 4,865 | 5,062 | Loleo Jaya | 8 | 6 | 97790 | Kasiruta |
| 82.04.15 | Kasiruta Barat (c) | West Kasiruta | 272.98 | 4,521 | 5,865 | 5,968 | Palamea | 10 | 25 | 97790 | Kasiruta |
Notes: (a) formally called Kepulauan Batanglomang; situated between Bacan and Mandioli Islands.
(b) except for Bobo desa, which has a postcode of 97792.
(c) includes Lata Lata Island (27.9 km2, with 1,201 inhabitants in 2020), located to the northwest of Kasiruta Island, and comprising two desa - Lata Lata and Sidanga.
Bacan Island's seven districts comprise 63 villages (desa) as follows: Bacan Timur Selatan - Liaro, Pigaraja, Silang, Tabajaya, Tabangame, Wayakuba and Wayaua. Batan Timur Tengah - Bibinoi, Songa, Tabapoma, Tawa, Tomara, Tutupa and Wayatim. Bacan Timur - Babang, Bori, Goro-Goro, Kaireu, Nyonyifi, Sabatang, Sali Kecil, Sayoang, Timlonga and Wayamiga. Bacan Selatan - Gandasuli, Kampung Makian, Kubung, Kupal, Mandaong, Panamboang, Papaloang, Sawadai, Tembal and Tuokona. Bacan (district) - Amasing Kali, Amasing Kota, Amasing Kota Barat, Amasing Kota Utara, Awanggoa, Belang Belang, Hidayat, Indomut, Kaputusan, Labuha, Marabose, Suma Tinggi, Sumae and Tomori. Bacan Barat Utara - Geti Baru, Geti Lama, Gilalang, Jojame, Lolarogurua, Nusa Babullah, Sidopo and Yaba. Bacan Barat - Indari, Kokotu, Kusubibi, Nang, Nondang, Tawabi and Wiring.
Batang Lomang's single district comprises 8 villages as follows: Bajo, Batutaga, Kampung Baru, Paisumbaos, Prapakanda, Sawangakar, Tanjung Obit and Toin.
Mandioli's two districts comprise 12 villages as follows: Mandioli Selatan - Bahu, Galala, Jiko, Lele, Tabalema and Yoyok. Mandioli Utara - Akedabo, Bobo, Indong, Leleongusu, Pelita and Waya.
Kasiruta's two districts comprise 18 villages, listed as follows with their populations in mid 2022: Kasirutu Barat - Kakupang (493), Marikapal (255), Bisori (671), Doko (809), Palamea (763), Arumamang (742), Lata Lata (640), Sidanga (631), Sengga Baru (455) and Imbu Imbu (437). Kasirutu Timur - Tawa Bacan Barat (639), Maritosa (893), Loleo Jaya (1,439), Kou Balabala (593), Loleo Mekar (437), Kasiruta Dalam (552), Jeret (374) and Tutuhu (262).
History
From early times, Bacan was one of the four kingdoms of Maluku together with Ternate, Tidore and Jailolo. The ruling elite converted to Islam in about the late 15th century. The sultan at first resided on Kasiruta Island and had political and commercial influence in northern Ceram and the Papuan Islands. In 1513, the first Portuguese trading fleet to reach the Moluccas set up a trading post on Bacan which at the time was tied to the Sultan of Ternate by dynastic marriages. The fleet's commander, Captain Antonio de Miranda Azevedo, left seven men on Bacan to buy cloves for the following year's expedition. Their arrogant behaviour and reported bad treatment of Bacan women led to their murder. As Ternate did not have enough stock, the ship for which the men had stayed to prepare was used by the Sultan of Ternate to fill Ferdinand Magellan's last ship, which was the first ship to circumnavigate the world. A slave and two birds of paradise were given to the ship by Bacan. Bacan became a place of refuge for rebellious Ternatans. The Portuguese sent a punitive expedition against Bacan but it failed, and instead the Portuguese Governor Galvão challenged Bacan's sultan to a duel to determine who was to be subservient to whom. The challenge was accepted but the duel never took place.[8]
In 1557, Father Antonio Vaz converted Bacan's sultan and court members to Catholicism. The king was married to a daughter of Sultan Hairun of Ternate. Fleets from Ternate invaded the islands in 1570 and later and the king apostatized in 1575, though he was nevertheless poisoned in 1578. A community of Christians remained and were later joined by coreligionists from Tobelo and Ambon. A small Roman Catholic hospital was built by an elderly Dutch nun. Today, Protestants significantly outnumber Catholics. During the mid-19th century Moluccan travels of British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace, Christians in the Moluccas were called Orang Sirani (lit. "Nazarene People"), a term regularly applied to locals of European ancestry in the Malay Archipelago, thought to have been descended from the Portuguese. They had dressed in white and black and Wallace reports they dance "quadrilles, waltzes, polkas, and mazurkas with great vigour and much skill".[8]
Following the 1575 Ternatan invasion, Bacan become subservient to Ternate for periods, which was sealed through marriages. A sister and a daughter of Sultan Saidi Berkat of Ternate married Bacan rulers in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. A Spanish fort was built in 1606. By this time the seat of the sultan had been moved from Kasiruta to Bacan Island. Once the Dutch East India Company established hegemony in 1609, the Netherlands' power on Bacan was based in Fort Barnaveld.[8]
In 1705, the sergeant in charge of the fort and the sultan captured the English explorer William Dampier, seized his ship, looted its cargo, and threatened all aboard with execution. It is thought that this was in response to Dampier violating the trade monopoly. When the sergeant's Dutch superiors heard of the incident, Dampier was released, his ship restored and the English provided with sumptuous hospitality in Ternate.[9] The chief town at the time, also known as Bachian, was Amasing or Amasingkota on the island's isthmus.[3]
Ternate and Bacan were the only places in the northern Moluccas that had a Dutch curriculum school and a Protestant minister in the late 19th century. The majority of Bacan's Roman Catholics became Protestants during the Dutch colonial period.[citation needed] These Sirani wore semi-European dress and celebrated Sundays with dancing and music.[3] The Sultanate of Bacan was treated as a Dutch protectorate;[3] it was replaced by a council of chiefs under a Dutch contrôleur in 1889.[2] A sultan with much reduced powers was eventually appointed in 1900. What independence remained was lost with the Japanese occupation during and Indonesian independence after World War II.[10] The most significant modern town is Labuha on the west coast. Bacan has more recently been in the news due to violence between Christian and Muslim inhabitants of the island.
Geography
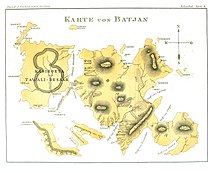
Bacan is of irregular form, consisting of two distinct mountainous parts, united by a low isthmus, which a slight subsidence would submerge.[3] The total land area is around 1,900 km2.[citation needed] The prevailing rocks are sandstone, coralline limestone, and pebbly conglomerate, although hot springs attest to volcanic activity as well.[3] The ancient and non-volcanic rocks are especially prevalent on the south side of the island.[2] The sulphur spring at Taubenkit has a temperature of 125 °F (52 °C) and a still more remarkable example is found at Sayowang on the east coast.[3] "Amasing Hill" on the northern half consists of three small andesitic volcanoes: Cakasuanggi, Dua Saudara, and Mount Sibela. The highest elevation on the southern half is Gunong Sabella[3] or Labua (6,950 ft or 2,120 m),[2] which the locals traditionally considered the seat of evil spirits.[3] Coal and other minerals have been discovered.[3]
During the 19th and early 20th century, large portions of the island were richly wooded, with indigenous sago, coconuts and cloves abundantly produced.[3][2] The Dutch purposefully exterminated the native nutmeg trees: a large grove still remained as late as the 1870s[3] but it had disappeared by the onset of World War I.[2] It is the easternmost point naturally inhabited by primates, in the form of a black macaque which also occurs on Sulawesi.[2] The world's largest bee, the giant mason bee, occurs here and on nearby Halmahera.
Demography
By the mid-19th century, the interior of Bacan island was considered uninhabited and the coastal dwellers all non-indigenous.[3] They consisted of the Christian descendants of Portuguese sailors (Sirani), of Malays and Papuans, of Galelas from northern Halmahera, and of Tomore people from Sulawesi's Bay of Tolo.[3] Prior to World War I, the population of the island was around 13 000, including some Chinese and Arabs.[2] In the late 1990s, 193 of Bacan's 7,700 Christians were Protestants.[10] The whole group had a population of 84,075 at the 2010 Census, but by mid 2023 had grown to 117,986.
Several non-Austronesian (Papuan) languages are spoken on Bacan, the main one of which is Galela but also Tobelo and Ternate. Near the capital Labuha, Bacanese Malay was once spoken, but as of 2012 it had only handful of speakers remaining.[11]
Economy
Colonial interest in Bacan was primarily driven by the spice trade, which was flourishing in Ternate, Tidore, and Halmahera. The island of Bacan was not particularly sought-after for its own resources, but rather, to assist control of the more valuable islands nearby. The Dutch East India Company paid a stipend to the Bacan sultan as compensation for the destruction of Bacan's clove trees that was higher than the salary of the Dutch Governor on Ternate and about 1/9 of that paid to the Sultan of Ternate.
It is thought that gold was washed on Bacan since at least 1774; in the mid-nineteenth century, 20 skilled Chinese gold workers were brought from west Borneo but a gold rush did not eventuate.[citation needed] During the era of steam power, an attempt was made to establish coal mining on the island[3] using Japanese convicts imprisoned by the Dutch. However, following the delivery of several tons the grade of coal was deemed poor and the mining was discontinued.
From 1882, an Amsterdam merchant cleared plantations for vanilla, coffee, tobacco and potatoes, however, his land was unsuitable and the crops succumbed to floods, drought, rot, insects and rodents. Despite over ten years of large investments of capital, creditors forced him out of business in 1900 although they also did not succeed with the plantations.[9] The indigenous economy included the gathering of pearl and mother-of-pearl, and the harvesting the resin from dammar.
See also
Notes
- ^ "Bacan | island, Indonesia". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 2020-02-18. Retrieved 2020-05-29.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i EB (1911), p. 132.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p EB (1878).
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica, 9th ed., Index, p. 39. 1889.
- ^ a b Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^ a b Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.
- ^ a b Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2024.
- ^ a b c Muller (1997), p. 130.
- ^ a b Muller (1997), p. 131.
- ^ a b Muller (1997), p. 132.
- ^ Bacanese Malay at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)

References
- Baynes, T. S., ed. (1878), , Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 3 (9th ed.), New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, p. 197
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911), , Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 3 (11th ed.), Cambridge University Press, pp. 132–133
- Muller, Karl (1997), Maluku: Indonesian Spice Islands, Singapore: Periplus Editions, ISBN 962-593-176-7
- Wessels, C. (1929) "De Katholieke missie in het Sultanaat Batjan (Molukken), 1667-1609", Historisch Tijdschrift 8:2 and 8:3
- Coolhaas, W.Ph. (1923) "Kronijk van het rijk Batjan", Tijdschrift voor Indische Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde 63.
