2S1 Gvozdika
| 2S1 (SAU-122) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Self-propelled artillery |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1972–present |
| Used by | see Operators |
| Wars | Soviet–Afghan War Iran–Iraq War Gulf War War in Abkhazia (1992–1993) Yugoslav Wars First Chechen War Second Chechen War Iraq War Russo-Georgian War First Libyan Civil War Second Libyan Civil War Syrian Civil War Russo-Ukrainian War Second Nagorno-Karabakh war Tigray War |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Kharkiv Tractor Plant |
| Designed | 1956–1961 |
| Produced | 1971–1991 |
| No. built | 10,000+ |
| Variants | see Variants |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 16 t (16 long tons; 18 short tons) |
| Length | 7.26 m (23 ft 10 in) |
| Barrel length | 4.27 m (14 ft 0 in)[1] |
| Width | 2.85 m (9 ft 4 in) |
| Height | 2.73 m (8 ft 11 in) |
| Crew | 4 |
| Shell | 122 x 447mm .R separate loading, cased charge |
| Caliber | 122 mm (4.8 in) |
| Breech | Horizontal sliding-wedge, semi-automatic |
| Elevation | -3 to +70 degrees |
| Traverse | 360 degrees |
| Rate of fire | Maximum: 5 rpm Sustained: 1–2 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 680 m/s (2,200 ft/s) |
| Maximum firing range | Conventional: 15.3 km (9.5 mi) Extended: 21.9 km (13.6 mi) |
| Armor | 7–20 mm (0.28–0.79 in) |
Main armament | 2A18 122 mm (4.8 in) howitzer |
| Engine | YaMZ-238N diesel 220 kW (300 hp) |
| Suspension | torsion bar |
Operational range | 500 km (310 mi) |
| Maximum speed | Road: 60 km/h (37 mph) Off-road: 30 km/h (19 mph) Swim: 4.5 km/h (2.8 mph) |
The 2S1 Gvozdika (Russian: 2С1 «Гвоздика», "Carnation") is a Soviet self-propelled howitzer introduced in 1972 and is in service in Russia and other countries as of 2024. It is based on the MT-LBu multi-purpose chassis, mounting a 122 mm 2A18 howitzer. "2S1" is its GRAU designation. An alternative Russian designation is SAU-122, but in the Russian Army it is commonly known as Gvozdika. The 2S1 is fully amphibious with very little preparation, and once afloat is propelled by its tracks. A variety of track widths are available to allow the 2S1 to operate in snow or swamp conditions. It is NBC protected and has infrared night-vision capability.
The 2S1 was developed in Kharkiv, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. It has seven road wheels on each side; the running gear can be fitted with different widths of track to match terrain. The interior is separated into a driver's compartment on the left, an engine compartment on the right and a fighting compartment to the rear. Within the fighting compartment the commander sits on the left, the loader on the right and the gunner to the front. The all-welded turret is located above the fighting compartment. The 2S1 uses a 122 mm howitzer based on the towed D-30 howitzer. The gun is equipped with a power rammer, a double-baffle muzzle brake and a fume extractor. It is capable of firing HE (high explosive), leaflet, HE/RAP, armor-piercing HE, flechette and chemical rounds.[2]
Production history
The first prototype was ready in 1958. The 2S1 entered service with the Soviet Army in the early 1970s and was first seen in public at a Polish Army parade in 1974. The vehicle was deployed in large numbers (72 per tank division, 36 per motorized rifle division). It was designated the M1974 by the U.S. Army and manufactured in Soviet, Polish and Bulgarian state factories.
Variants
Iran
- Raad-1 ('Thunder') – Iranian variant based on the hull of the Boragh APC.
Myanmar
- 2S1U – In March 2019, a Ukrainian company, the Great Export Import Company, and the Myanmar military have signed a joint-venture agreement to build a plant capable of manufacturing armored personnel carriers (APCs) and self-propelled howitzers. The types of APCs that will be made in the plant are said to be eight-wheeled BTR-4Us while the howitzers will be 2S1Us, which are based on the MT-LBu multipurpose chassis.[3][4]
Poland
The 2S1 Gvozdika, and other related vehicles such as the MT-LB and Opal, were produced in Poland by Huta Stalowa Wola under the name 2S1 Goździk.
- 2S1M Goździk – Version with special amphibious kit that increases the vehicle's amphibious capabilities.
- 2S1T Goździk – Version with a TOPAZ digital fire control system from WB Electronics. The system consists of a FONET-IP digital intercom system, new digital radio, military GPS receiver, military computer and dedicated software. The same system is used on other Polish Armed Forces artillery systems like the AHS Krab, Dana-T and WR-40 Langusta.
Romania
- OAPR model 89 (Obuzierul autopropulsat românesc, model 89) – Romanian variant combining the 2S1 Gvozdika's turret and a modified version of the MLI-84's chassis. Designed around 1978, it was produced between 1987 and 1992. Also, it is simply known as Model 89.[5][6]
Russia
- 2S34 Khosta – Modernisation of the 2S1 with the 122 mm 2A31 gun replaced by the 120 mm 2A80-1 gun-mortar. Further improvements include a new Malakhit fire control system, a battlefield observation system and the ability to fire the Kitolov-2M guided ammunition. One unit, the 21st Guards Motor Rifle Brigade in Totskoye, is currently[when?] being equipped with the system.[citation needed]
Serbia
- 2S1 modernized - The modernization is being carried out on the basis of the 122 mm towed howitzer of the Serbian modernization program. Project "SORA 122mm" and NORA B-52. Where the truck platform was abandoned, which was used by the prototype version of the "SORA 122mm" system in favor of a much better, crawler platform 2S1 Gvozdika system. The action was made possible by two new projectiles and an increased range of about 40% from 15,200 to 22,000 m (9.4 to 13.7 mi). A new ballistic computer and fire control system make it much faster to prepare for action. There is also a new inertial navigation system, GPRS, as well as the possibility of action, multiple projectiles in one point, MRSI. Thus, it was achieved that with one 2S1 Gvozdika system, in the system of MRSI action in one point, 6 projectiles can be fired in one minute; the modernized 2S1 Gvozdika is much improved. For better defense, a turret with a 12.7 mm machine gun was added. In 2021, the first modernized 2S1 Gvozdika system battery was inducted into service with the Serbian Army.
Soviet Union
- 2S15 Norov – A prototype tank destroyer equipped with a radar-based fire control system and a 100 mm gun.[7]
- UR-77 Meteorit – Mine clearing vehicle with launcher for mine-clearing line charges.
Ukraine
- Kevlar-E – Infantry fighting vehicle based on the 2S1 platform, equipped with Shturm remote weapon station and room for 6 passengers in addition to the 3 crew. The original 220 kW (300 hp) V8 diesel engine has been replaced with a 310 kW (420 hp) diesel engine produced by Caterpillar, Cummins or Deutz, increasing the maximum road speed to 70 km/h (43 mph). The vehicle is amphibious and has air conditioning, a fire detection and suppression system, an NBC system, navigation system, and night-vision equipment. The variant was first introduced in April 2018.[8] The prototype has been fighting in the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[9]
- On January 21, 2025, the Danish Ministry of Defense quietly added the 2S1 Gvozdika 122mm self-propelled howitzer to its list of military donations to Ukraine. The quantity remains unspecified, and the origin of these systems has not been disclosed.[10]
Vietnam
- PTH-01/122 – Local version of 2S1 Gvozdika
Operators
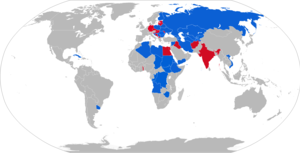





Current operators
 Algeria – 140 as of 2024[11]
Algeria – 140 as of 2024[11] Angola − 9+ as of 2024[12]
Angola − 9+ as of 2024[12] Armenia – 9 as of 2024[13]
Armenia – 9 as of 2024[13] Azerbaijan − 68 as of 2024[14]
Azerbaijan − 68 as of 2024[14] Belarus – 125 as of 2024[15]
Belarus – 125 as of 2024[15] Bulgaria – 48 as of 2024[16]
Bulgaria – 48 as of 2024[16] Chad – 10 as of 2024[17]
Chad – 10 as of 2024[17] Congo-Brazzaville − 3 as of 2024[18]
Congo-Brazzaville − 3 as of 2024[18] Congo-Kinshasa − 6 as of 2024[19]
Congo-Kinshasa − 6 as of 2024[19] Cuba[20]
Cuba[20] Croatia – 8 as of 2024[21]
Croatia – 8 as of 2024[21] Eritrea – 32 as of 2024[22]
Eritrea – 32 as of 2024[22] Ethiopia[23]
Ethiopia[23] Finland – 74 as of 2024[24]
Finland – 74 as of 2024[24] Georgia − 20 as of 2024[25]
Georgia − 20 as of 2024[25]
Hezbollah − Used in Syria[26]
 Iran − 60+ 2S1 and Raad-1 as of 2024[27]
Iran − 60+ 2S1 and Raad-1 as of 2024[27] Kazakhstan – 60 as of 2024[28]
Kazakhstan – 60 as of 2024[28] Kurdistan − Unknown number operated by the Peshmerga[29]
Kurdistan − Unknown number operated by the Peshmerga[29] Kyrgyzstan − 18 as of 2024[30]
Kyrgyzstan − 18 as of 2024[30] Libya − Used by the Libyan National Army[31]
Libya − Used by the Libyan National Army[31] Poland – 206 as of 2024[32]
Poland – 206 as of 2024[32] Romania − 6 2S1 and 34 Model 89 as of 2024[33]
Romania − 6 2S1 and 34 Model 89 as of 2024[33] Russia – 130 used by the Ground Forces, 85 used by the Naval Infantry, plus an unknown amount operated by the 1st Army Corps, 2nd Army Corps, and border guards. Estimated to have 1,800 in storage as of 2024[34]
Russia – 130 used by the Ground Forces, 85 used by the Naval Infantry, plus an unknown amount operated by the 1st Army Corps, 2nd Army Corps, and border guards. Estimated to have 1,800 in storage as of 2024[34] Serbia – 67 as of 2024[35]
Serbia – 67 as of 2024[35] Sudan[36]
Sudan[36] South Sudan[37]
South Sudan[37] Syria[38]
Syria[38] Tajikistan − 3 as of 2024[39]
Tajikistan − 3 as of 2024[39] Turkmenistan – 40 as of 2024 [40]
Turkmenistan – 40 as of 2024 [40] Ukraine – 125+ used by the Ground Forces, Marines and Airborne Assault Troops as of 2024[41]
Ukraine – 125+ used by the Ground Forces, Marines and Airborne Assault Troops as of 2024[41] Uruguay – 6 as of 2024[42]
Uruguay – 6 as of 2024[42] Uzbekistan − 18 as of 2024[43]
Uzbekistan − 18 as of 2024[43] Vietnam[44]
Vietnam[44] Yemen[45]
Yemen[45] Zimbabwe − 12 as of 2024[46]
Zimbabwe − 12 as of 2024[46]
Former operators
 Czech Republic – 91 in 1999[47]
Czech Republic – 91 in 1999[47] Czechoslovakia – 230 in 1989.[48] Passed on to successor states
Czechoslovakia – 230 in 1989.[48] Passed on to successor states East Germany – 300 in 1989.[49] Phased out in 1990 after German reunification
East Germany – 300 in 1989.[49] Phased out in 1990 after German reunification Hungary[50]
Hungary[50] Iraq – Unknown number operational prior to the 2003 invasion of Iraq[51]
Iraq – Unknown number operational prior to the 2003 invasion of Iraq[51] Islamic State[52]
Islamic State[52] Libya − 130 in 2004[53]
Libya − 130 in 2004[53] Republika Srpska − 24 in 2004[54]
Republika Srpska − 24 in 2004[54] Slovakia[55]
Slovakia[55] Slovenia – 8 in 1999[56]
Slovenia – 8 in 1999[56] Soviet Union – 3,200 used by the Ground Forces and 90 by the Naval Infantry in 1989.[57] Passed on to successor states
Soviet Union – 3,200 used by the Ground Forces and 90 by the Naval Infantry in 1989.[57] Passed on to successor states Yugoslavia – Passed on to successor states[58]
Yugoslavia – Passed on to successor states[58]
Combat history
- Afghanistan – Soviet–Afghan War
- Chechnya (Russia) – First Chechen War (1994–1996), Second Chechen War (1999 to 2000)
- Iraq – Iran–Iraq War, Gulf War, Iraq War
- Yugoslavia – Yugoslav Wars
- Georgia – Russo-Georgian War
- Libya – First Libyan Civil War, Second Libyan Civil War
- Nagorno-Karabakh - Second Nagorno-Karabakh War
- Syria – Syrian Civil War[59]
- Ukraine – Russo-Ukrainian War
See also
- PLZ-07 – type of Self-propelled artillery
- PLZ-89 – Chinese 122 mm self-propelled howitzer
- 122 mm howitzer 2A18 (D-30) – Soviet 122 mm towed artillery
- 2S19 Msta – Soviet/Russian 152 mm self-propelled howitzer
- 2S3 Akatsiya – Soviet 152 mm self-propelled howitzer
- 2S35 Koalitsiya-SV – Russian 152 mm self-propelled artillery
- List of artillery
- List of AFVs
Bibliography
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (1989). The military balance, 1989-1990. London: Brassey's. ISBN 978-0080375694.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (1999). The Military Balance 1999-2000. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-922425-8.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2004). Langton, Christopher (ed.). The Military Balance 2004/2005. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-856622-9.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2024). The Military Balance 2024. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-040-05115-3.
- Trewhitt, Philip (1999). Armored Fighting Vehicles. New York, NY: Amber Books. p. 124. ISBN 0-7607-1260-3.
References
- ^ Investments, M. (n.d.). 2S1-gvozdika. Mortar. Retrieved November 13, 2022, from https://mortarinvestments.eu/catalog/item/2s1-gvozdika
- ^ Marat Kenzhetaev (1998). "Self Propelled Artillery and Mortars". armscontrol.ru. MIPT Center for Arms Control, Energy and Environmental Studies. Archived from the original on 10 January 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2010.
- ^ "myanmar-ukrainian firming aims plant deal". 9 March 2019.
- ^ "Joint venture to supply Ukrainian APCs to Myanmar army | March 2019 Global Defense Security army news industry | Defense Security global news industry army 2019 | Archive News year". www.armyrecognition.com.
- ^ http://www.worldwar2.ro/documents/004-artileria-romana-in-date-si-imagini.pdf p. 164
- ^ "Obuzierul Autopropulsat Românesc, Model 1989". 23 June 2018.
- ^ "САУ 2С15 "Норов". СССР". Archived from the original on 21 April 2014. Retrieved 9 May 2014.
- ^ Foss, Christopher F (29 April 2018). "Ukraine re-roles 2S1 SPH for infantry combat". IHS Jane's 360. London. Archived from the original on 1 May 2018. Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- ^ Axe, David (28 March 2023). "Ukraine Made Exactly One Oddball Kevlar-E Fighting Vehicle. It's Been Battling Around Kharkiv For A Year". Forbes. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ^ https://armyrecognition.com/focus-analysis-conflicts/army/conflicts-in-the-world/russia-ukraine-war-2022/exclusive-denmark-strengthens-ukraines-artillery-with-a-discreet-delivery-of-2s1-gvozdika-self-propelled-howitzers
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 343.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 471.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 178.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 180.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 183.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 77.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 481.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 482.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 486.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 428.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 79.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 490.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 491.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 89.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 185.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 369.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 353.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 186.
- ^ International Institute for Strategic Studies (February 2016). The Military Balance 2016. Vol. 116. Routledge. p. 491. ISBN 9781857438352.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 188.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 371.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 125.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 131.
- ^ IISS 2024, pp. 193, 198, 201, 205.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 133.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 521.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 520.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 386.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 207.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 209.
- ^ IISS 2024, pp. 212−214.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 452.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 215.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 324.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 394.
- ^ IISS 2024, p. 529.
- ^ IISS 1999, p. 51.
- ^ IISS 1989, p. 46.
- ^ IISS 1989, p. 47.
- ^ IISS 2004, p. 55.
- ^ Cordesman, Anthony H. (7 February 2003). Iraqi Armed Forces on the Edge of War (PDF) (Report). Center for Strategic and International Studies. p. 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 February 2010. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- ^ Mitzer, Stijn; Oliemans, Joost. "Vehicles and equipment captured by the Islamic State inside Syria until November 2014". Oryx Blog.
- ^ IISS 2004, p. 130.
- ^ IISS 2004, p. 84.
- ^ IISS 2004, p. 68.
- ^ IISS 1999, p. 97.
- ^ IISS 1989, pp. 34, 37.
- ^ Kočevar, Iztok (August 2014). "Micmac à tire- larigot chez Tito: L'arme blindée yougoslave durant la Guerre froide" [The Yugoslav armored arm during the Cold War]. Batailles et Blindés (in French). No. 62. Caraktère. pp. 66–79. ISSN 1765-0828.
- ^ "- YouTube". www.youtube.com.
External links
 Media related to 2S1 Gvozdika at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 2S1 Gvozdika at Wikimedia Commons- FAS.org
- Armscontrol.ru
- Huta Stalowa Wola – Polish manufacturer
- Arsenal Co. – Bulgarian manufacturer of 2A31(2S1)
